When it comes to choosing the right battery for your needs, you might find yourself stuck between lead acid and lithium ion options. Both have their strengths and weaknesses, but which one truly fits your lifestyle and power demands?
Understanding the key differences can save you money, boost your device’s performance, and even keep you safe. You’ll discover how lead acid and lithium ion batteries compare on cost, lifespan, efficiency, and safety—helping you make a smart choice that powers your world without compromise.
Keep reading to unlock the facts that most people overlook before buying a battery.
Credit: www.relionbattery.com
Lead Acid Batteries
Lead acid batteries have powered many devices and vehicles for over a century. They remain popular due to their reliability and low cost. These batteries store energy through chemical reactions involving lead and sulfuric acid. Despite newer options, lead acid batteries still serve many needs effectively.
Basic Structure And Chemistry
Lead acid batteries consist of lead dioxide and sponge lead plates. These plates sit in a sulfuric acid electrolyte. During discharge, lead dioxide reacts with sulfuric acid to produce electrical energy. When charging, this process reverses. The battery’s design allows for easy recycling of materials.
Performance Characteristics
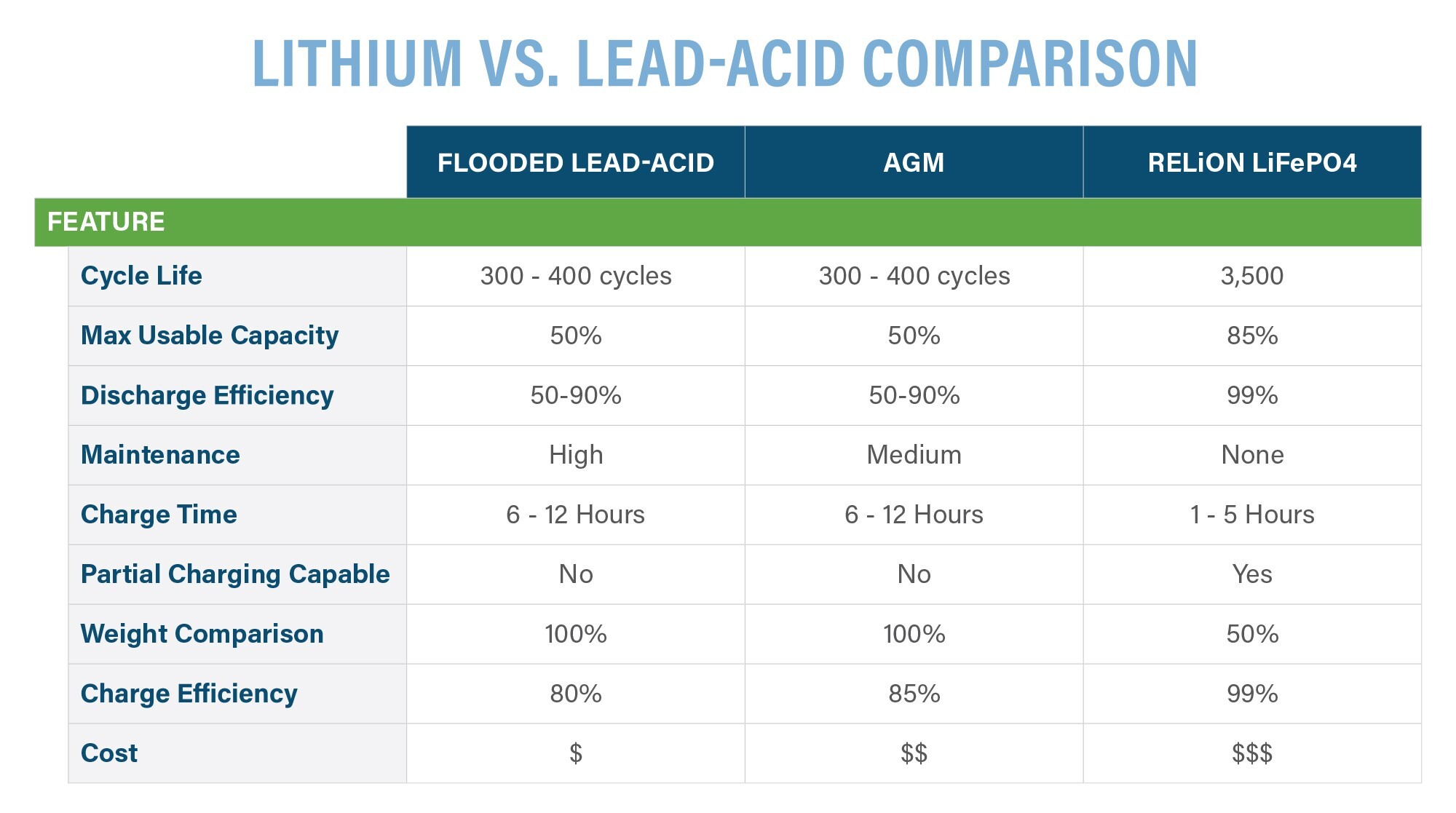
Lead acid batteries provide steady voltage and high surge currents. They perform well in cold temperatures but have lower energy density than lithium-ion types. Their cycle life is shorter, usually around 300 to 500 cycles. Charging time can be longer, and they require maintenance to avoid damage.
Common Applications
These batteries power cars, motorcycles, and backup power systems. They serve in solar energy storage and uninterruptible power supplies (UPS). Lead acid batteries are common in industrial machines and golf carts. Their ability to deliver high current makes them suitable for starting engines.
Advantages And Limitations
Lead acid batteries cost less upfront and have a simple design. They are widely available and easy to recycle. Their main limitations include heavy weight and lower energy density. Maintenance needs and shorter lifespan also affect usability. Safety risks are lower compared to some newer batteries.
Lithium Ion Batteries
Lithium ion batteries have become popular in many devices due to their lightweight and high performance. These batteries store electrical energy using lithium ions that move between electrodes during charge and discharge. Their advanced design supports longer usage and faster charging compared to older battery types.
They power everything from smartphones to electric vehicles, offering a balance of power and size. Understanding their core parts and how they work helps explain their benefits and challenges.
Core Components And Chemistry
Lithium ion batteries consist of three main parts: the anode, cathode, and electrolyte. The anode is usually made of carbon, while the cathode contains lithium metal oxides. The electrolyte carries lithium ions between these two electrodes during use. This movement of ions creates the electric current that powers devices. The chemistry involves lithium ions moving back and forth, which is efficient and stable under normal conditions.
Energy Density And Efficiency
These batteries have high energy density, meaning they store more energy in a smaller space. This feature allows devices to run longer without increasing battery size. They also have excellent efficiency, losing less energy during charging and discharging. This efficiency translates to longer battery life per charge and less heat generation, making them safer and more reliable for daily use.
Typical Uses
Lithium ion batteries are common in portable electronics like phones, laptops, and tablets. They also power electric vehicles and energy storage systems for homes and businesses. Their lightweight design and high capacity make them ideal for applications requiring mobility and long run times. Even drones and medical devices depend on these batteries for reliable power.
Strengths And Drawbacks
These batteries offer many advantages, including low weight, high energy density, and longer life compared to lead acid types. They charge faster and have less memory effect, which means they maintain capacity better over time. On the downside, they can pose safety risks such as overheating and fire if damaged or improperly charged. They also cost more and require careful recycling due to toxic materials used in their construction.
Energy And Power Comparison
Comparing energy and power between lead acid and lithium ion batteries reveals key differences. These differences affect how each battery performs in daily use and specific applications. Understanding these factors helps choose the right battery type.
Energy and power metrics determine battery strength, endurance, and efficiency. Both types serve well but excel in different areas.
Capacity And Density Differences
Lithium ion batteries have higher energy density than lead acid batteries. This means they store more energy in a smaller, lighter package. Lead acid batteries are heavier and bulkier due to their design. Capacity-wise, lithium ion offers more usable capacity, often over 80%. Lead acid batteries usually provide about 50% usable capacity before damage risk.
Charge And Discharge Rates
Lithium ion batteries charge faster and handle high discharge rates better. They can deliver power quickly without damage. Lead acid batteries require slower charging to avoid harm. Their discharge rates are lower, limiting performance in high power demand situations. Fast charging and discharging make lithium ion ideal for devices needing quick energy bursts.
Efficiency In Various Conditions
Lithium ion batteries maintain efficiency in a wide range of temperatures. They lose less energy during charging and discharging cycles. Lead acid batteries suffer efficiency drops in cold weather and under heavy loads. Their chemical reactions slow down, reducing output. Lithium ion’s stable performance suits diverse environments and uses.
Lifespan And Durability
The lifespan and durability of batteries significantly affect their overall value and usability. Choosing between lead acid and lithium ion batteries requires understanding how long each type lasts and how well it endures daily use. Battery longevity impacts replacement costs and system reliability. Durability influences performance under different conditions and usage patterns.
This section explains key aspects of battery lifespan and durability. It covers how many charge cycles each battery type can handle, what causes them to degrade, and their maintenance needs. These factors help users decide which battery suits their needs best.
Cycle Life Expectations
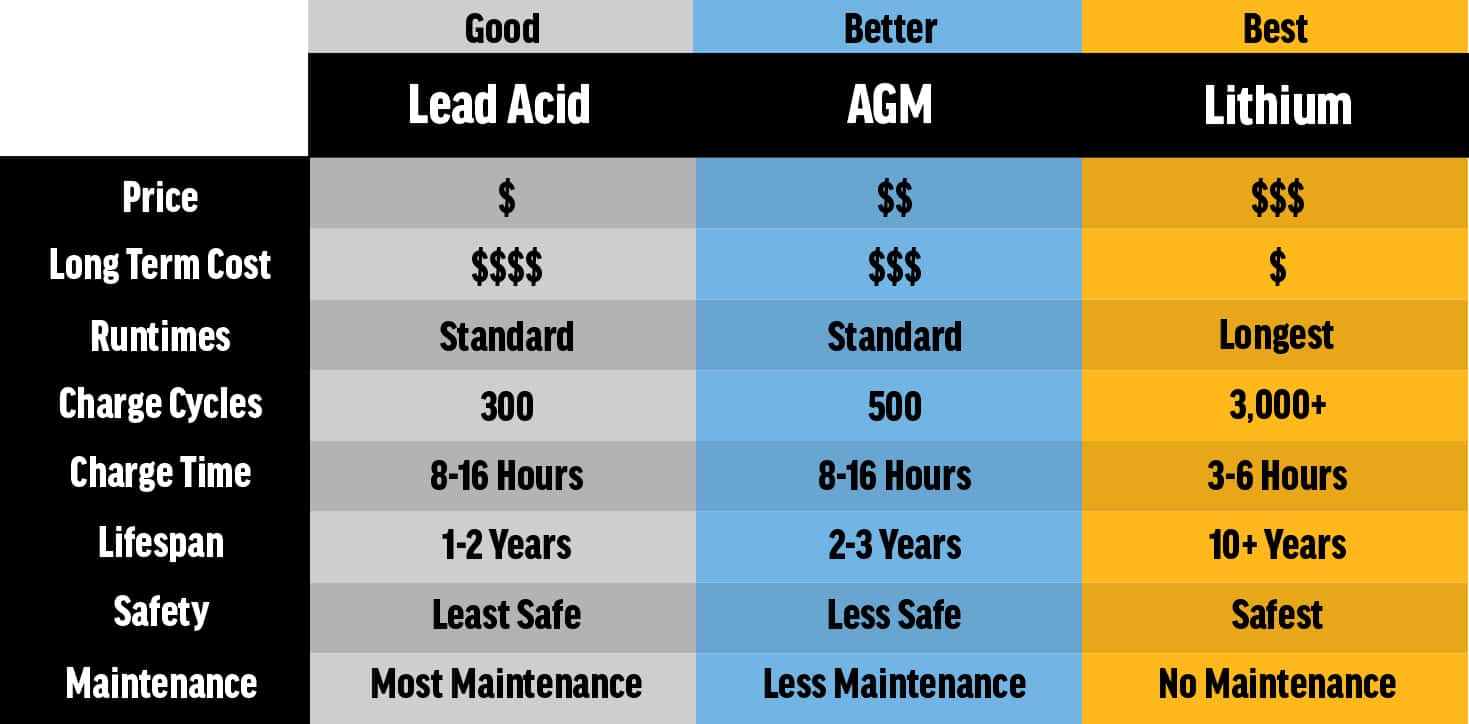
Lead acid batteries usually offer between 300 and 500 cycles. Their cycle life depends on depth of discharge and charging habits. Lithium ion batteries can often exceed 2000 cycles. This makes lithium ion a better choice for long-term use. More cycles mean longer battery life and fewer replacements.
Degradation Factors
Lead acid batteries degrade faster if deeply discharged often. High temperatures and sulfation also reduce their lifespan. Lithium ion batteries degrade mainly due to high temperatures and overcharging. Both types lose capacity over time. Proper use slows degradation and extends battery life.
Maintenance Needs
Lead acid batteries require regular maintenance. They need water refills and cleaning to prevent corrosion. Checking voltage and ensuring full charge helps avoid damage. Lithium ion batteries need very little maintenance. They do not require watering or equalizing charges. Proper care still helps maximize their lifespan.
Safety And Risks
Safety and risks are vital factors when choosing between lead acid and lithium ion batteries. Each battery type carries unique hazards that users must understand. Proper knowledge helps prevent accidents and ensures safe operation.
Thermal Runaway In Lithium Batteries
Thermal runaway is a dangerous reaction in lithium ion batteries. It happens when the battery gets too hot. Heat causes internal reactions that create even more heat. This cycle can lead to fires or explosions.
Damage to the battery, overcharging, or manufacturing defects often start thermal runaway. High temperatures in the environment may also trigger it. Once started, the reaction spreads quickly inside the battery.
Fire And Explosion Hazards
Both lead acid and lithium ion batteries can catch fire, but lithium ion batteries are more prone. The chemicals inside lithium batteries are flammable. If the battery is damaged or misused, it may ignite or explode.
Lead acid batteries contain acid that can leak and cause burns but are less likely to catch fire. Fires from lithium ion batteries burn hotter and are harder to control. This risk makes careful handling essential.
Handling And Usage Precautions
Always use the correct charger for your battery type. Avoid overcharging or deep discharging batteries. Keep batteries away from heat and direct sunlight. Do not puncture, crush, or expose batteries to physical damage.
Store batteries in a cool, dry place. Inspect batteries regularly for signs of swelling or leaks. Dispose of damaged or old batteries safely at designated recycling centers. Following these steps reduces safety risks significantly.

Credit: www.tycorun.com
Environmental Impact
Batteries power many devices and vehicles today. Their environmental impact matters for our planet’s health. Lead acid and lithium ion batteries differ in how they affect the environment. Examining material toxicity, resource extraction, and recycling shows their true impact.
Material Toxicity And Disposal
Lead acid batteries contain lead, a toxic metal harmful to humans and animals. Improper disposal can pollute soil and water. Acid inside these batteries can cause burns and damage ecosystems.
Lithium ion batteries hold metals like lithium, cobalt, and nickel. These materials are toxic if leaked. They can harm both people and wildlife. Safe disposal is essential to prevent pollution.
Resource Extraction Concerns
Mining lead for batteries damages land and uses a lot of energy. It can release harmful dust and chemicals into the air and water. Mining cobalt and lithium has similar issues, plus concerns about worker conditions.
Extracting lithium often requires large amounts of water. This can dry out local areas and harm plants and animals. Responsible mining practices help reduce these problems but are not always followed.
Recycling Challenges And Solutions
Lead acid batteries have well-established recycling systems. Most lead is recovered and reused, lowering new mining needs. Recycling helps reduce pollution and saves energy.
Lithium ion battery recycling is more complex and less common. Recovering lithium and other metals is harder and costly. New technologies aim to improve lithium battery recycling rates to protect resources and reduce waste.
Cost Analysis
Cost analysis plays a key role in choosing between lead acid and lithium ion batteries. Understanding their costs helps make smarter investments. This section breaks down costs into initial purchase, long-term value, and supply chain trends. Each factor affects overall expenses differently.
Initial Purchase Costs
Lead acid batteries have lower upfront prices than lithium ion. This makes them attractive for tight budgets. Lithium ion batteries cost more initially due to advanced materials and technology. The higher price reflects better energy density and longer lifespan. Buyers should weigh upfront cost against performance needs.
Long-term Value And Roi
Lithium ion batteries offer greater long-term value. Their longer cycle life reduces replacement frequency. They also maintain capacity better over time, saving money on replacements. Lead acid batteries need more frequent replacements and maintenance. This adds to total ownership cost. Calculating return on investment favors lithium ion for many uses.
Supply Chain And Market Trends
Lithium ion battery prices fluctuate with raw material availability like lithium and cobalt. Demand for electric vehicles drives market growth and innovation. Lead acid batteries use common materials with stable supply and pricing. Supply chain risks differ between types, impacting cost stability. Staying aware of trends helps plan purchases wisely.
Installation And Replacement
Installing and replacing batteries requires careful attention to several factors. Both lead acid and lithium ion batteries have unique needs during installation. Choosing the right battery type affects performance and safety. Understanding compatibility, switching steps, and technical needs helps ensure a smooth process.
Compatibility Considerations
Lead acid and lithium ion batteries differ in size and voltage. Check if the new battery fits the existing space. Confirm the battery terminals match the device connections. Some systems may need adapters or modifications. Battery management systems (BMS) must also support the new battery type. Ignoring compatibility can damage equipment or reduce battery life.
Switching From Lead Acid To Lithium
Switching from lead acid to lithium involves more than swapping batteries. Lithium batteries need different charging profiles and protections. Remove the old lead acid battery carefully to avoid acid spills. Install the lithium battery with correct polarity and secure mounting. Update or replace the charger to one designed for lithium cells. Test the system fully before regular use to avoid failures.
Technical Requirements
Lithium ion batteries require specific chargers to control voltage and current. The battery management system must monitor temperature and charge levels. Wiring may need upgrades to handle different current flows. Ventilation is less critical than for lead acid but still necessary. Follow manufacturer guidelines strictly to maintain safety and battery life. Professional installation is recommended for complex systems.
Future Trends
The battery industry is evolving rapidly, with new trends shaping the future of lead acid and lithium ion batteries. These trends focus on making batteries safer, more efficient, and environmentally friendly. Innovations in technology aim to extend battery life and reduce costs. The next generation of batteries promises to support cleaner energy and smarter devices.
Advancements In Battery Technology
Researchers work on increasing energy density for both battery types. Lithium ion batteries are seeing improvements in charging speed and capacity. Lead acid batteries get enhanced designs for longer cycle life. Solid-state batteries, a new option, may offer better performance and durability. These advances help meet growing energy needs in electric vehicles and renewable systems.
Improved Safety Measures
Safety remains a top priority in battery development. Lithium ion batteries now include better thermal management systems. New electrolytes reduce the risk of fire and explosion. Lead acid batteries benefit from improved sealing and ventilation methods. Smart battery management systems detect faults early. These features protect users and extend battery lifespan.
Sustainability Innovations
Recycling methods for batteries are becoming more efficient and widespread. Efforts focus on recovering valuable materials like lead, lithium, and cobalt. Lead acid batteries have a high recycling rate, often above 95%. Lithium ion recycling is improving but still faces challenges. Manufacturers explore eco-friendly materials to reduce environmental impact. Sustainable production and disposal help conserve resources for the future.
Credit: www.axcs.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Is A Lithium-ion Battery Better Than Lead-acid?
Lithium-ion batteries offer higher energy density, longer life, and better efficiency than lead-acid batteries. They are lighter but cost more. Safety risks like fire exist, requiring careful use and management.
What Is The Biggest Disadvantage Of A Lithium-ion Battery?
The biggest disadvantage of a lithium-ion battery is its risk of fire and explosion from thermal runaway caused by damage, overcharging, or heat.
Can I Just Replace A Lead-acid Battery With Lithium?
You cannot directly replace a lead-acid battery with lithium without checking compatibility. Lithium batteries need proper chargers and battery management systems. They offer better efficiency but require specific installation to ensure safety and performance. Always consult manufacturer guidelines before switching battery types.
Do Lead-acid Or Lithium Batteries Last Longer?
Lithium batteries generally last longer than lead-acid batteries, offering more charge cycles and better energy efficiency.
Conclusion
Choosing between lead acid and lithium ion batteries depends on your needs. Lead acid batteries cost less and are simple to use. Lithium ion batteries last longer and weigh less. They store more energy and charge faster. Safety is important; lithium batteries need careful handling.
Both types have pros and cons. Think about budget, usage, and safety before deciding. This helps you pick the right battery for your device or vehicle. Understanding these differences makes your choice clearer and smarter.















