Are you wondering if diesel engines really last longer than gasoline ones? If you’re thinking about buying a diesel vehicle or just curious about how these engines hold up over time, this article is for you.
Diesel engines have a reputation for durability and long life, but is that always true? You’ll discover the key reasons why diesel engines might outlast their gasoline counterparts—and also the challenges they face along the way. By the end, you’ll have a clear picture to help you decide if a diesel engine is the right choice for your needs.
Keep reading to uncover the facts behind diesel engine longevity!
Diesel Engine Longevity
Diesel engines are known for their long-lasting performance. They often run for hundreds of thousands of miles. This makes them popular for heavy-duty vehicles and trucks.
Their longevity depends on many factors. These include how the engine is built, maintained, and used. Understanding these can help you see why diesel engines last longer.
Durability Factors
Diesel engines face higher pressure than gasoline engines. They are built to handle this stress. Stronger parts reduce wear and tear over time.
Diesel fuel also acts as a lubricant. It helps reduce friction inside the engine. This lowers damage and extends engine life.
Engine Design And Materials
Manufacturers use tougher materials in diesel engines. Heavy-duty steel and iron parts resist heat and pressure better. The design focuses on strength and reliability.
Diesel engines have fewer moving parts than gasoline engines. This means fewer chances of mechanical failure. The design also allows for easier repairs and maintenance.
Typical Lifespan Compared To Gasoline
Diesel engines usually last longer than gasoline ones. They often reach 300,000 to 500,000 miles with proper care. Gasoline engines typically last 150,000 to 200,000 miles.
Diesel engines run at lower RPMs (revolutions per minute). This reduces wear and helps the engine last longer. Many drivers choose diesel for this reason.
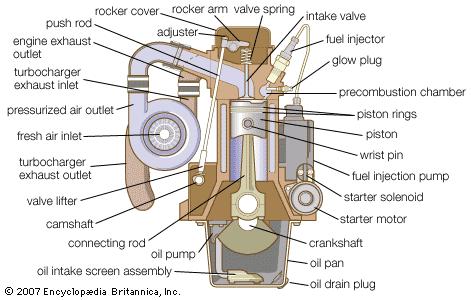
How Diesel Engines Work
Diesel engines operate differently than gasoline engines. They rely on a unique method to ignite fuel. This method makes diesel engines strong and durable. Understanding how diesel engines work helps explain why they often last longer.
Compression Ignition Process
Diesel engines use compression ignition to start. Air is compressed inside the cylinder. This compression raises air temperature to a high level. Then, diesel fuel is injected into the hot air. The fuel ignites instantly from the heat. No spark plugs are needed in this process. This method creates a powerful combustion that drives the engine.
Fuel Efficiency Mechanisms
Diesel engines burn fuel more efficiently than gasoline engines. The high compression ratio helps extract more energy from fuel. Diesel fuel contains more energy per gallon than gasoline. Engines adjust fuel injection precisely to save fuel. This efficiency means diesel engines use less fuel for the same work. The result is better mileage and longer engine life.
Heat And Pressure Effects
Diesel engines run under higher heat and pressure than gasoline engines. Their parts are built to handle this stress. Stronger engine blocks and pistons resist wear over time. The intense pressure helps burn fuel completely, reducing deposits. These conditions lead to slower engine wear. The engine lasts longer with proper care and maintenance.
Advantages Of Diesel Engines
Diesel engines hold many benefits that make them popular in various vehicles and machinery. Their design and operation bring several advantages that often lead to longer engine life. Understanding these benefits helps explain why diesel engines are trusted for heavy-duty use and long-term reliability.
The advantages cover aspects like fuel efficiency, power delivery, and engine durability. These factors contribute to better performance and lower costs over time. Let’s explore some key benefits of diesel engines.
Fuel Economy Benefits
Diesel engines use fuel more efficiently than gasoline engines. They extract more energy from each drop of fuel. This means they can travel farther on less fuel. Diesel fuel also contains more energy per gallon. This results in better mileage and fewer stops at the pump. Fuel economy makes diesel engines cost-effective for long-distance driving and heavy loads.
Torque And Power Characteristics
Diesel engines produce high torque at low speeds. Torque is the force that helps vehicles move heavy loads. This makes diesel engines ideal for trucks and machinery. They provide strong pulling power without needing high engine speeds. The steady power delivery improves control and safety. Diesel engines handle tough driving conditions with ease.
Lower Engine Wear
Diesel engines operate at lower RPMs than gasoline engines. This reduces stress and wear on engine parts. The combustion process in diesel engines is slower and more controlled. It causes less heat and pressure on components. Diesel engines use stronger materials designed for durability. These factors help diesel engines last longer and require fewer repairs.
Credit: www.capitalremanexchange.com
Common Diesel Engine Drawbacks
Diesel engines offer strong performance and durability. Yet, they come with some drawbacks. Understanding these common issues helps in making a smart choice. These challenges affect cost, comfort, and environmental impact.
Below are some typical diesel engine drawbacks. Each can influence your experience and expenses.
Higher Initial Costs
Diesel engines usually cost more to buy than gasoline engines. This higher price is due to tougher engine parts and advanced fuel systems. The upfront cost can be a barrier for many buyers.
Maintenance and repair costs may also be higher. Diesel parts tend to be stronger but pricier to replace. This impacts the total ownership cost over time.
Fuel Availability Challenges
Diesel fuel is not as widely available as gasoline in some areas. This can make refueling harder during trips. Remote locations might have limited diesel stations.
Fuel quality can vary, affecting engine performance and longevity. Using poor-quality diesel may cause damage or reduce efficiency.
Noise And Vibration Issues
Diesel engines create more noise and vibration than gasoline engines. This can lead to a rougher and less comfortable ride. Noise reduction technology helps but does not eliminate it fully.
For some drivers, this extra noise can cause fatigue on long drives. Vibrations may also affect cabin comfort.
Cold Start Difficulties
Diesel engines often face problems starting in cold weather. They require extra heat to ignite fuel properly. Glow plugs or block heaters are sometimes needed.
Cold starts can strain the engine and battery, increasing wear. This issue is more common in regions with harsh winters.
Emission Concerns
Diesel engines produce higher levels of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and soot particles. These pollutants contribute to air pollution and health risks. Governments enforce strict emission rules on diesel vehicles.
Meeting these standards requires complex emission control systems. These systems add cost and maintenance needs. Diesel engines may also face restrictions in certain cities.
Maintenance And Care Tips
Proper maintenance and care play a key role in how long a diesel engine lasts. Diesel engines are built tough, but they need regular attention to stay in good shape. Small habits and timely checks can prevent big problems. This section shares simple tips to keep your diesel engine running smoothly for years.
Regular Service Importance
Regular service keeps diesel engines healthy and efficient. Change oil and filters on time to avoid engine wear. Check fuel filters to stop dirt from entering the system. Inspect belts and hoses for cracks or leaks. Servicing helps spot issues early and saves money on repairs.
Emission System Upkeep
Diesel engines have special emission systems to reduce pollution. Keep the diesel particulate filter (DPF) clean to prevent clogging. Use quality diesel fuel to protect the emission parts. Regularly check sensors and the exhaust system. Proper upkeep helps the engine run cleaner and last longer.
Handling Short Trips
Diesel engines perform best when fully warmed up. Short trips cause buildup of soot and fuel residue. Avoid many quick trips in a row. Let the engine run at operating temperature to burn off deposits. This habit reduces engine stress and extends its life.
Preventing Common Failures
Some diesel engine parts fail more often than others. Watch the fuel injectors and turbochargers for signs of trouble. Use additives to keep fuel clean and prevent corrosion. Replace worn-out glow plugs for easier starts. Taking these steps lowers risk of costly breakdowns.

Credit: 4btengines.com
Modern Diesel Technology
Modern diesel technology has improved many aspects of diesel engines. These advances help diesel engines run cleaner, quieter, and more efficiently. They also increase engine lifespan by reducing wear and tear. Innovations focus on emission control, noise reduction, and fuel delivery systems. Each improvement plays a key role in making diesel engines more reliable and durable.
Emission Reduction Innovations
New technologies reduce harmful emissions from diesel engines. Systems like Diesel Particulate Filters (DPF) trap soot before it leaves the exhaust. Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) uses a special fluid to cut nitrogen oxide (NOx) gases. These tools help diesel engines meet strict environmental rules. Cleaner emissions mean less engine damage over time.
Noise And Vibration Improvements
Diesel engines used to be noisy and rough. Modern designs reduce engine noise with better insulation and engine mounts. Advanced balancing techniques lower vibration levels inside the engine. These changes make diesel vehicles quieter and smoother. Less vibration also means less stress on engine parts, boosting longevity.
Fuel Injection Advances
Fuel injection systems have become highly precise. Common rail technology sprays fuel in fine, controlled bursts. This improves combustion, making the engine more efficient. Better fuel delivery reduces carbon buildup inside the engine. Cleaner combustion helps diesel engines last longer and perform better.
Diesel Vs Gasoline Engines
Diesel and gasoline engines serve different needs and preferences. Each type has unique strengths and weaknesses that affect engine life and user experience. Understanding these differences helps choose the right engine for specific requirements.
Performance Comparison
Diesel engines deliver more torque at low speeds. This trait suits heavy-duty tasks and towing. Gasoline engines offer higher horsepower for faster acceleration. They perform well in lighter vehicles and daily commuting. Diesel engines run at lower RPMs, causing less wear over time. Gasoline engines operate at higher RPMs, which may cause quicker wear.
Cost Over Vehicle Lifetime
Diesel vehicles often cost more upfront than gasoline models. Fuel efficiency of diesel engines reduces fuel expenses over time. Maintenance costs for diesel can be higher due to complex components. Gasoline engines usually have lower initial costs and simpler maintenance. Overall, diesel may be cheaper long-term for high-mileage use.
Suitability For Different Uses
Diesel engines excel in trucks, buses, and heavy machinery. They handle long distances and heavy loads well. Gasoline engines suit passenger cars and short trips better. Diesel engines need to reach optimal temperature for efficiency. Gasoline engines start easily in cold weather and short drives. Choice depends on driving habits and vehicle purpose.
Surprising Facts About Diesel Engines
Diesel engines hold a unique place in the world of vehicles. Many believe they last longer than gasoline engines. Some facts about diesel engines might surprise you. Understanding these facts helps clear up common doubts and myths.
Myths Vs Reality
Many say diesel engines always outlast gasoline ones. The truth varies with use and care. Diesel engines have stronger parts built to handle high pressure. This can mean longer life under proper maintenance. Yet, neglect or harsh driving can shorten their lifespan. Not all diesel engines are equal; design and quality matter.
Unexpected Longevity Stories
There are stories of diesel engines running over 500,000 miles. Some trucks and buses keep going beyond a million miles. These engines often run at steady speeds and lower RPMs. Such conditions reduce wear and extend engine life. Regular oil changes and timely repairs play a key role. These tales show diesel engines can last very long.
Common Misconceptions
People often think diesel engines are noisy and dirty. Modern diesel engines are quieter and cleaner than before. Many assume diesel fuel is hard to find. Diesel is widely available in most places. Some believe diesel engines are slow. New diesel models offer good power and speed. These myths do not hold true today.

Credit: www.youtube.com
Conclusion
Diesel engines often last longer than gasoline engines due to their sturdy design. They handle wear and heat better, which helps increase lifespan. Regular care and proper maintenance keep them running smoothly. Despite higher upfront costs and fuel expenses, many find diesel engines reliable for long-term use.
Noise and emissions can be drawbacks, but technology continues to improve these issues. Choosing between diesel and gasoline depends on your driving needs and budget. Overall, diesel engines offer durability that suits many drivers well.