Have you ever wondered what actually powers your car’s start every time you turn the key? Your car battery is the hidden hero that makes it all happen.
Without it, your engine won’t crank, your lights won’t shine, and your electronics won’t work. Understanding how a car battery works can save you from unexpected breakdowns and costly repairs. You’ll discover the simple science behind your car battery’s power, how it charges and discharges, and the key signs that it might be failing.
Keep reading to unlock the secrets of your car’s power source and learn how to keep it running strong.
Car Battery Basics
A car battery is vital for starting the engine and powering electrical parts. It stores energy and delivers it when the car needs a strong electrical boost. Understanding how it works helps you maintain it better and avoid unexpected breakdowns.
This section explains the basic parts, the chemical reaction inside, and the battery’s voltage and capacity. These basics give you a clear picture of your car battery’s role.
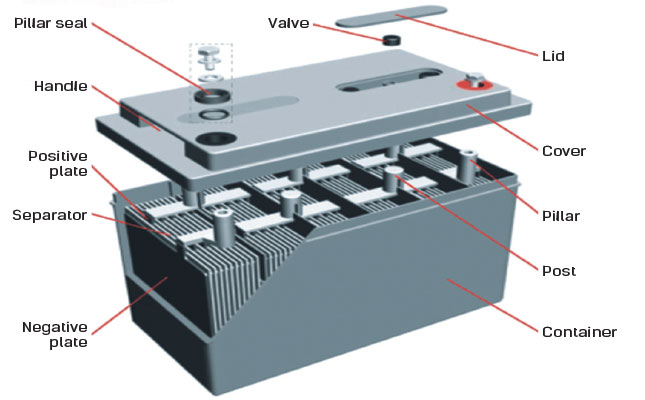
Battery Components
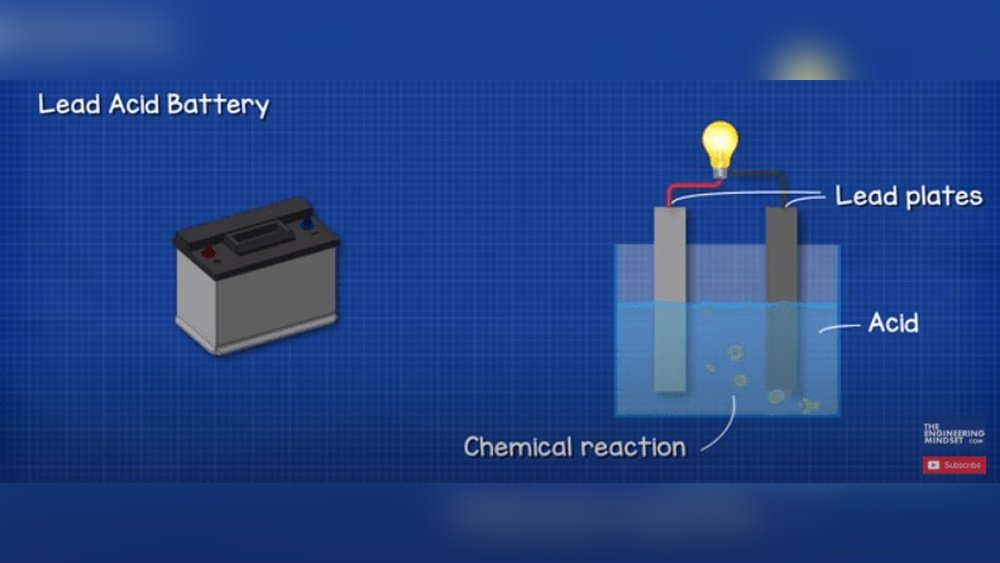
A car battery has several key parts. The main parts are the positive and negative plates. These plates are inside a case filled with electrolyte fluid. Terminals connect the battery to the car’s electrical system. A casing protects all these parts from damage.
Chemical Reaction Inside
The battery works by a chemical reaction between the plates and the electrolyte. This reaction creates electrical energy. When the engine starts, the battery sends power through this reaction. It changes chemicals back and forth to store and release energy.
Voltage And Capacity
Most car batteries have 12 volts. This voltage is enough to start the engine and run electronics. Capacity shows how much charge the battery can hold. It is measured in ampere-hours (Ah). Higher capacity means the battery lasts longer before needing a recharge.

Credit: theengineeringmindset.com
Power Generation Process
The power generation process in a car battery is essential for starting the engine and running electrical systems. It involves chemical reactions that produce electrical energy. This energy powers the car’s starter motor, lights, and other electronics.
Understanding this process helps to know how the battery charges and discharges, keeping the vehicle running smoothly.
Charging Mechanism
The car battery charges through the alternator. The alternator converts mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy. This energy flows to the battery, restoring its charge. The battery stores this energy for future use. Charging keeps the battery ready to start the car at any time.
Discharging Mechanism
Discharging happens when the battery powers the car’s electrical parts. The battery releases stored electrical energy through a chemical reaction. This energy runs the starter motor and other devices. Over time, the battery loses charge and needs recharging to keep working.
Role Of Electrolytes
Electrolytes are fluids inside the battery. They allow the flow of electrical charges between the battery’s plates. This flow creates the chemical reactions needed for power generation. Electrolytes play a key role in both charging and discharging processes. Proper electrolyte levels ensure the battery works efficiently.
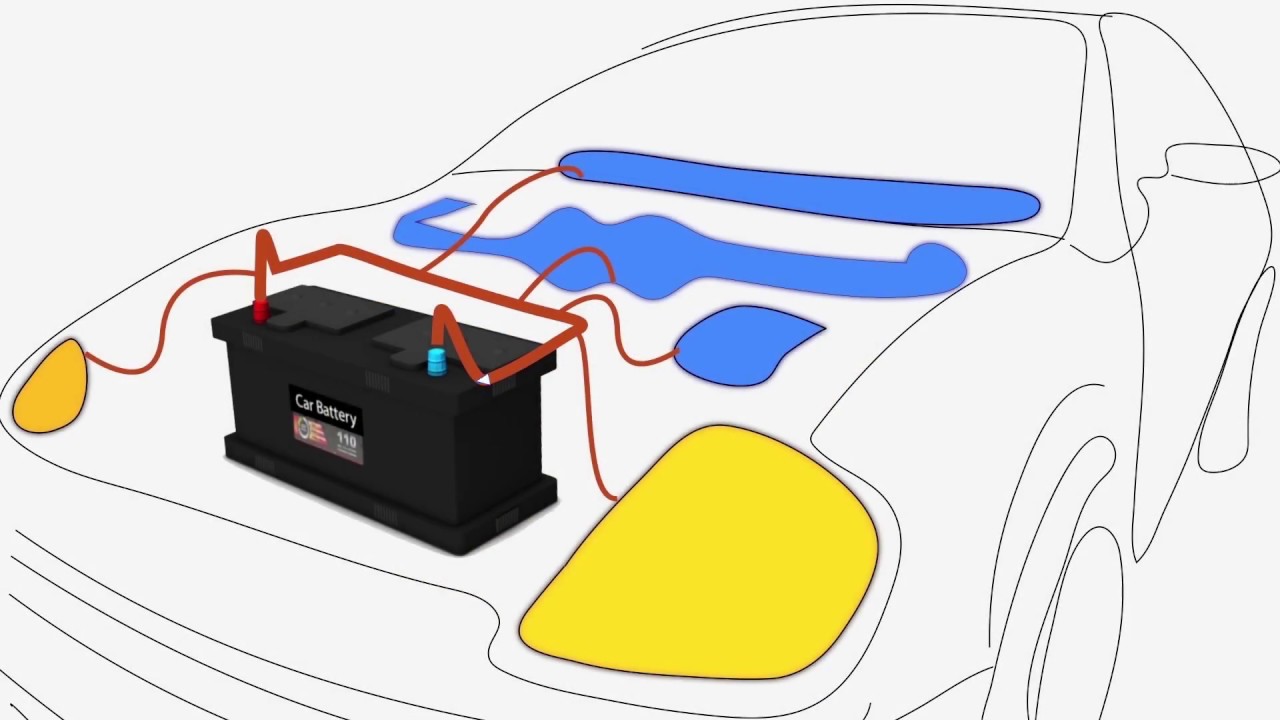
Battery And Engine Interaction
The car battery and engine work closely to power your vehicle. The battery stores electrical energy. It delivers this energy to start the engine. After the engine starts, the battery also powers other systems. These include lights, radio, and sensors. The engine and battery depend on each other for smooth operation.
Starting The Engine
The battery sends a large burst of power. This power goes to the starter motor. The starter motor turns the engine’s crankshaft. This action begins the engine’s internal combustion process. Without enough power from the battery, the engine will not start.
Supplying Power To Electronics
While the engine runs, the battery supports the car’s electronics. It powers devices like headlights, dashboard lights, and the radio. The battery ensures these systems work even when the engine’s power fluctuates. It acts as a steady source of electricity for electronics.
Alternator’s Role
The alternator recharges the battery while driving. It converts mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy. The alternator also powers electrical systems during the drive. This process keeps the battery charged and ready for the next start. Without the alternator, the battery would quickly drain.
Signs Of Battery Issues
Car batteries are vital for starting your vehicle and powering electrical systems. Recognizing signs of battery issues helps avoid unexpected breakdowns. Early detection ensures safety and saves money on repairs.
Slow Engine Crank
The engine may turn over slowly or struggle to start. This happens when the battery cannot supply enough power. You might hear a sluggish or labored sound during ignition. Slow cranks often mean the battery is weak or near failure.
Dim Or Flickering Lights
Headlights and interior lights might appear dimmer than usual. Flickering lights can also occur when the battery’s voltage drops. This happens because the battery cannot maintain a steady electrical flow. Such signs suggest the battery is losing its charge capacity.
Frequent Jump-starts
Needing to jump-start your car often points to a battery problem. A healthy battery should hold a charge for a long time. Regular jump-starts show the battery struggles to store or deliver power. This issue requires immediate attention to prevent getting stranded.
Dashboard Warning Lights
The battery or charging system warning light may appear on the dashboard. This light alerts you to potential battery or alternator problems. Ignoring these warnings can lead to complete battery failure. Check the battery and charging system promptly if this light comes on.
Physical Battery Problems
Physical battery problems often cause car battery failure. These issues affect battery performance and lifespan. Recognizing physical signs helps prevent complete battery breakdown. Some common physical problems include corroded terminals, swollen cases, and unusual smells.
Corroded Terminals
Corroded terminals appear as white or blue powder on battery posts. Corrosion blocks electrical flow between the battery and cables. This causes poor engine starts and weak electrical systems. Cleaning terminals with a mixture of baking soda and water often fixes this. Always disconnect the battery before cleaning to avoid shocks.
Swollen Battery Case
A swollen battery case looks bloated or misshapen. Heat or overcharging causes the battery to expand. Swelling signals internal damage and reduces battery efficiency. It also increases the risk of leaks or explosions. A swollen battery must be replaced immediately for safety reasons.
Unusual Smells
Unusual smells near the battery often indicate a problem. A rotten egg or sulfur smell means battery acid is leaking. Acid leaks can damage car parts and pose health risks. This smell requires urgent attention and battery inspection. Never ignore strange odors coming from your battery.
Battery Maintenance Tips
Proper battery maintenance helps your car battery last longer. It keeps the battery reliable and avoids unexpected failures. Simple care steps improve battery performance and save money on replacements.
Regular checks and cleaning ensure good electrical connection. Protecting the battery from harsh conditions also prevents damage. Follow these tips for a healthy car battery.
Cleaning Terminals
Dirty or corroded terminals block power flow. Use a wire brush to clean the battery terminals carefully. Remove any white, green, or blue corrosion buildup. After cleaning, apply a thin layer of petroleum jelly. This prevents future corrosion and keeps terminals shiny.
Checking Electrolyte Levels
Some batteries have removable caps for checking fluid levels. The electrolyte should cover the battery plates inside. If low, add distilled water, not tap water. Avoid overfilling as it may cause spills. Check levels every few months to keep the battery healthy.
Protecting From Extreme Temperatures
High heat speeds up battery wear and fluid loss. Cold weather reduces battery power and slows chemical reactions. Park your car in a shaded or covered area. Use an insulated battery blanket in winter to keep warmth. These steps help maintain battery strength year-round.
When To Replace Your Battery
Knowing when to replace your car battery is important for smooth vehicle operation. Batteries wear out over time and stop holding a charge well. Replacing a battery at the right time helps avoid unexpected breakdowns. Watch for signs that your battery is weakening to act quickly. Regular checks keep your car reliable and safe.
Typical Battery Lifespan
Most car batteries last between three to five years. Climate and driving habits affect this lifespan. Hot weather can shorten battery life by causing fluid evaporation. Cold weather may reduce battery power temporarily. Regular short trips may prevent full recharging, stressing the battery more. Knowing the average lifespan helps plan for replacement before failure.
Performance Decline Indicators
Slow engine starts are a common battery problem sign. The engine may crank slowly or click without starting. Headlights and interior lights may dim when the engine runs. You might notice a strong smell like rotten eggs near the battery. Corroded or swollen battery terminals also show battery trouble. Frequent jump-starts indicate the battery cannot hold charge well.
Professional Testing Methods
Mechanics use special tools to test battery health. A load tester checks if the battery can hold voltage under pressure. A multimeter measures voltage and current output. Some shops offer free battery testing during routine service. Testing helps confirm battery condition before replacement. It also ensures the charging system works properly with the battery.
Credit: www.youtube.com
Credit: www.farmersweekly.co.za
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does A Car Recharge Its Battery?
A car recharges its battery using the alternator, which converts engine power into electrical energy while driving. The alternator powers electronics and replenishes the battery’s charge simultaneously.
How Do You Know If A Car Battery Needs Replacing?
A car battery needs replacing if the engine cranks slowly, headlights dim, jump-starts increase, warning light shows, terminals corrode, case swells, or it emits a rotten egg smell.
What Is The Correct Order To Jump Start A Car Battery?
Connect the positive jumper cable to the dead battery’s positive terminal. Attach the other end to the good battery’s positive terminal. Connect the negative cable to the good battery’s negative terminal. Finally, attach the other end to an unpainted metal surface on the dead car’s engine.
What Drains A Car Battery When The Car Is Off?
Parasitic drains like alarm systems, interior lights, and electronic modules consume battery power when the car is off.
Conclusion
A car battery powers your vehicle’s electrical system. It stores energy and provides a strong start. The battery works by a chemical reaction inside its cells. The alternator recharges the battery while driving. Regular checks help keep the battery healthy and long-lasting.
Understanding this helps you maintain your car better. A well-functioning battery means fewer surprises on the road. Simple care extends battery life and improves performance. Now you know how a car battery works and why it matters.