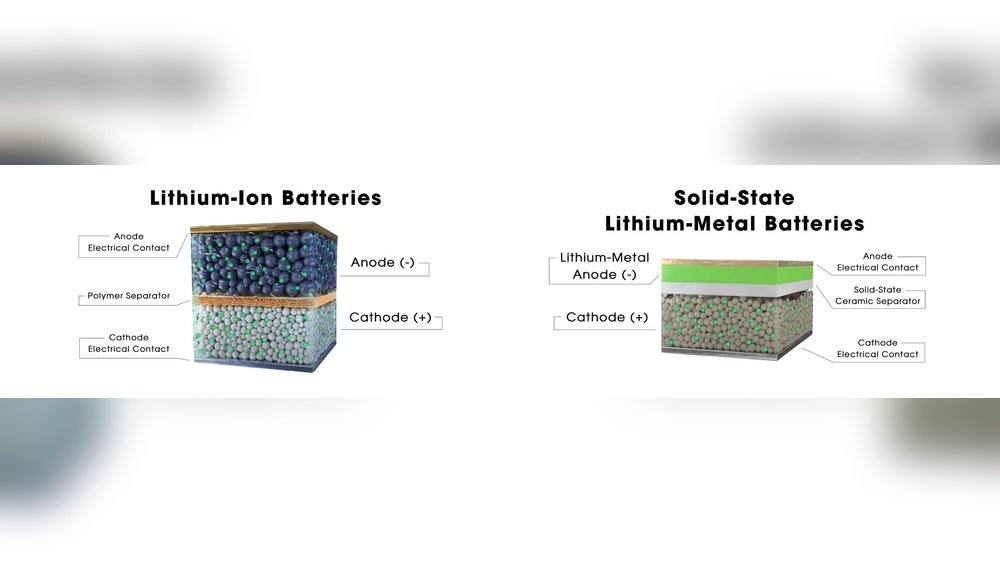
If you’ve ever wondered what powers the future of electric cars and smart devices, understanding solid state batteries is key. These batteries promise to be safer, last longer, and store more energy than the ones you’re used to.
But what exactly is a solid state battery, and why is everyone talking about it? You’re about to discover how this technology works, why it could change everything, and what challenges still stand in the way. Keep reading to find out how solid state batteries might soon power your life in ways you never imagined.
Solid State Battery Basics
Solid state batteries are an advanced type of battery technology. They offer a new way to store and use energy. Understanding their basics helps to see why they matter in today’s world.
This technology replaces the liquid or gel electrolyte found in traditional batteries with a solid material. This change leads to many benefits, such as improved safety and longer battery life.
What Makes It Different
Unlike traditional lithium-ion batteries, solid state batteries use a solid electrolyte. This solid layer conducts ions between the battery’s electrodes. It removes the risk of leaks and fires caused by liquid electrolytes.
The solid electrolyte also allows for higher energy density. This means the battery can store more power in the same space. It also tends to last longer with less capacity loss over time.
Another key difference is the battery’s stability. Solid state batteries resist dendrite growth, which can cause short circuits in liquid-based batteries. This makes them safer and more reliable.
Key Components
Solid state batteries have three main parts: the anode, cathode, and solid electrolyte. The anode stores lithium ions when the battery charges. The cathode releases ions during discharge.
The solid electrolyte separates the anode and cathode. It allows ions to move between them while blocking electrons. This process generates the electric current that powers devices.
Materials used in the solid electrolyte vary. Common options include ceramics, glass, or solid polymers. Each material offers different strengths in conductivity, stability, and flexibility.
Energy Density Advantages
Solid state batteries offer higher energy density than traditional batteries. This means they can store more energy in the same space. Higher energy density allows devices to run longer without increasing battery size. It also improves the efficiency of energy storage. These benefits make solid state batteries attractive for many uses.
Energy density is a key factor in battery performance. Increasing it can lead to lighter and smaller batteries. This change can affect many industries, especially electric vehicles and portable electronics. The advantages of solid state batteries in energy density open new possibilities for future technology.
Higher Capacity Benefits
Solid state batteries can hold more charge than lithium-ion batteries. They use solid electrolytes, which are safer and allow tighter packing of materials. This setup increases the battery’s total capacity. More capacity means longer battery life and fewer charges needed. It also supports higher power output for demanding tasks.
Devices using these batteries can be slimmer and lighter. This is important for phones, laptops, and wearable technology. The higher capacity also reduces the need for frequent battery replacements. It helps users save money and reduces electronic waste.
Impact On Electric Vehicles
Electric vehicles (EVs) benefit greatly from solid state batteries. Higher energy density means EVs can travel farther on a single charge. This reduces range anxiety for drivers. It also lowers the battery weight, improving vehicle efficiency and handling.
Faster charging is possible due to better battery chemistry. This shortens downtime and makes EVs more convenient. Solid state batteries also increase safety by reducing fire risks. These advantages support the growth and adoption of electric vehicles worldwide.
Safety Improvements
Solid state batteries offer major safety improvements over traditional batteries. They use solid electrolytes instead of liquid ones. This change reduces risks linked to battery fires and chemical leaks. These batteries are more stable and less likely to fail under stress. Safety is a key reason why many experts see solid state batteries as the future of energy storage.
Reduced Fire Risks
Traditional batteries use liquid electrolytes that can catch fire if damaged. Solid state batteries replace this liquid with a solid material. This solid electrolyte does not burn or leak easily. It lowers the chance of short circuits and overheating. Less fire risk means safer devices and electric vehicles.
Stable Electrolytes
Solid electrolytes are more chemically stable than liquids. They resist breaking down even at high temperatures. This stability helps prevent dangerous reactions inside the battery. Solid electrolytes also reduce the formation of dendrites. Dendrites can cause battery failure and fires in liquid-based batteries. Overall, stable electrolytes improve the battery’s lifespan and safety.
Manufacturing Complexities
Manufacturing solid state batteries involves many complex steps. These batteries use solid electrolytes instead of liquid ones. This change demands new methods and precise controls. The process is more delicate and requires advanced technology. Many manufacturers face challenges in making these batteries cost-effectively and at scale.
Advanced Production Techniques
Solid state batteries need special production techniques. One method is sintering, which fuses materials at high temperatures. Another is thin-film deposition, layering materials very thinly. These processes require precise temperature and pressure control. Equipment for these steps is expensive and not widely available. Small errors can cause defects that reduce battery performance.
Scaling Challenges
Scaling production from lab to factory is difficult. Making large batteries for electric vehicles needs uniform quality over big areas. Maintaining solid electrolyte contact without gaps or cracks is a major problem. Mechanical stress during battery use can cause damage. High material costs and complex assembly slow down mass production. Manufacturers work to improve yield and reduce waste to lower costs.
Material Challenges
Solid-state batteries promise higher energy and safety than traditional batteries. Yet, material challenges slow their progress. These challenges affect battery life, performance, and cost. Understanding them helps explain why solid-state batteries are not yet common.
Interfacial Resistance Issues
Solid-state batteries use solid electrolytes instead of liquid ones. This change creates resistance at the interface between the electrolyte and electrodes. Poor contact reduces ion flow, lowering battery efficiency. Tiny gaps or rough surfaces worsen this resistance. Scientists work to improve interfaces for better conductivity.
Dendrite Formation
Dendrites are tiny, needle-like structures that grow inside batteries. They form when lithium deposits unevenly during charging. In solid-state batteries, dendrites can pierce the solid electrolyte. This causes short circuits and battery failure. Preventing dendrite growth is key for safety and battery life.
Electrolyte Sensitivities
Solid electrolytes are sensitive to temperature and moisture. High heat can degrade materials quickly. Moisture can react with electrolytes, causing damage. These sensitivities require strict manufacturing and handling conditions. Finding stable electrolyte materials remains a major research focus.

Credit: www.batterypowertips.com
Mechanical Stress Factors
Mechanical stress plays a critical role in solid state battery performance. It affects the battery’s lifespan and safety. Stress arises due to physical changes inside the battery during charging and discharging cycles. Understanding these factors helps improve battery design and durability.
Volume Expansion Effects
Solid state batteries undergo volume changes as ions move in and out of electrodes. This expansion and contraction cause internal pressure on battery materials. Repeated volume changes can weaken the structure and reduce efficiency. Managing volume expansion is essential to prevent mechanical failure.
Cracking And Contact Loss
Mechanical stress can lead to cracks in the solid electrolyte or electrodes. Cracks break the physical contact between components, increasing resistance and lowering battery performance. Contact loss can cause hot spots and reduce battery life. Designers aim to minimize cracking for stable, long-lasting batteries.
Thermal Management
Thermal management is critical for solid state batteries. These batteries generate heat during charge and discharge. Proper control of temperature ensures safety and performance. Overheating can damage the battery or reduce its lifespan. Cooling systems and materials help manage this heat effectively. Maintaining stable temperatures allows the battery to work efficiently and last longer.
Heat Dissipation Limits
Solid state batteries have strict heat dissipation limits. Their solid electrolytes conduct less heat than liquid ones. This can cause heat to build up inside the battery. Excess heat may lead to swelling or internal damage. Designers use special materials to improve heat flow. Cooling plates and heat sinks help remove heat quickly. Managing heat keeps the battery stable during fast charging and heavy use.
Cold Climate Solutions
Cold weather can reduce solid state battery performance. Low temperatures slow down chemical reactions inside the battery. This lowers the battery’s capacity and power output. Heating elements are often built into the battery pack. These keep the battery warm enough for normal operation. Insulating materials also protect against cold air. Effective thermal management ensures the battery works well in winter and cold regions.

Credit: www.britannica.com
Performance And Durability
Solid state batteries promise higher performance and longer life than traditional batteries. Their durability depends on many factors, including materials and design. Understanding their cycle life and industry standards helps clarify their current state and future potential.
Cycle Life Concerns
Cycle life means how many times a battery can charge and discharge. Solid state batteries face challenges with cycle life. The solid electrolyte can crack or degrade after many cycles. This leads to reduced capacity and efficiency. Mechanical stress from volume changes also harms the battery’s lifespan. Researchers work to improve materials to extend cycle life. Yet, long-term data is limited as these batteries are still new.
Lack Of Industry Standards
Industry standards guide battery testing and safety measures. Solid state batteries lack widely accepted standards today. This slows development and market adoption. Different manufacturers use varied materials and methods. Without common rules, comparing performance is hard. Standardization will help ensure quality and reliability. It will also boost consumer trust and safety. Organizations and companies are starting to create these standards now.
Current Applications
Solid state batteries are moving beyond labs into real-world uses. Their unique design offers better safety and longer life. Industries now test these batteries in different devices. Early adoption shows promise despite some production challenges.
Prototype Vehicles
Many car makers use solid state batteries in prototype vehicles. These batteries store more energy in less space. They help cars run longer on a single charge. Safety improves since solid electrolytes reduce fire risk. Testing in prototypes helps fix design and production issues. This phase is crucial before mass production begins. Some electric cars on the road already use early versions. These trials guide future electric vehicle (EV) battery development.
Consumer Electronics
Solid state batteries also power consumer electronics. Devices like smartphones, laptops, and wearables benefit from their compact size. They charge faster and last longer than standard batteries. Reduced overheating risk makes them safer for daily use. Manufacturers experiment with these batteries to improve product life. This tech could soon replace lithium-ion batteries in gadgets. Early models show better performance and user experience. Consumers may see more devices with solid state batteries soon.
Future Outlook
The future of solid state batteries holds great promise for energy storage. These batteries offer higher safety and energy capacity. Many experts believe they will change how we power devices and vehicles. Yet, challenges remain in making them practical and affordable. Ongoing research and development aim to solve these issues. The coming years may see important progress toward widespread use.
Research Breakthroughs
Scientists have made important discoveries in solid state battery materials. New solid electrolytes show better conductivity and stability. Researchers focus on reducing dendrite growth that harms battery life. Advances in manufacturing methods improve battery consistency and performance. Many labs test different designs to find the best balance of power and durability. These breakthroughs bring solid state batteries closer to real-world use.
Commercialization Timelines
Experts expect early solid state batteries in niche markets soon. Small devices and luxury electric vehicles may use them first. Mass production for everyday electric cars will take more time. Industry leaders predict wider commercial use within five to ten years. Scaling up manufacturing remains a key challenge. Costs must drop for solid state batteries to compete with current options.
Credit: www.flashbattery.tech
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Problem With Solid-state Batteries?
Solid-state batteries face challenges like complex manufacturing, high costs, poor electrode contact, dendrite formation, mechanical stress, and scaling difficulties.
Does Tesla Use Solid-state Batteries?
Tesla does not currently use solid-state batteries in its vehicles. The company relies on advanced lithium-ion battery technology. Solid-state batteries face manufacturing and cost challenges that limit mass production. Tesla continues researching solid-state options but focuses on improving existing battery designs for now.
How Soon Will Solid-state Batteries Be Available?
Solid-state batteries may reach commercial availability within 3 to 5 years. Mass production faces cost and technical challenges. Researchers actively work on scaling and improving stability for electric vehicles.
Are Solid-state Batteries Better Than Lithium?
Solid-state batteries offer higher energy density and improved safety compared to lithium-ion batteries. They face manufacturing and cost challenges. Lithium-ion batteries remain more established and affordable today. Solid-state technology shows promise but is not yet widely available or fully proven for mass use.
Conclusion
Solid state batteries offer many benefits over traditional types. They use solid electrolytes, which improve safety and energy storage. Yet, challenges remain in making them affordable and reliable. Scientists work hard to solve these issues every day. As research moves forward, solid state batteries may become common.
This technology could change how we power devices and vehicles. For now, understanding their basics helps us see the future clearly. Keep an eye on solid state battery progress—it’s worth watching.